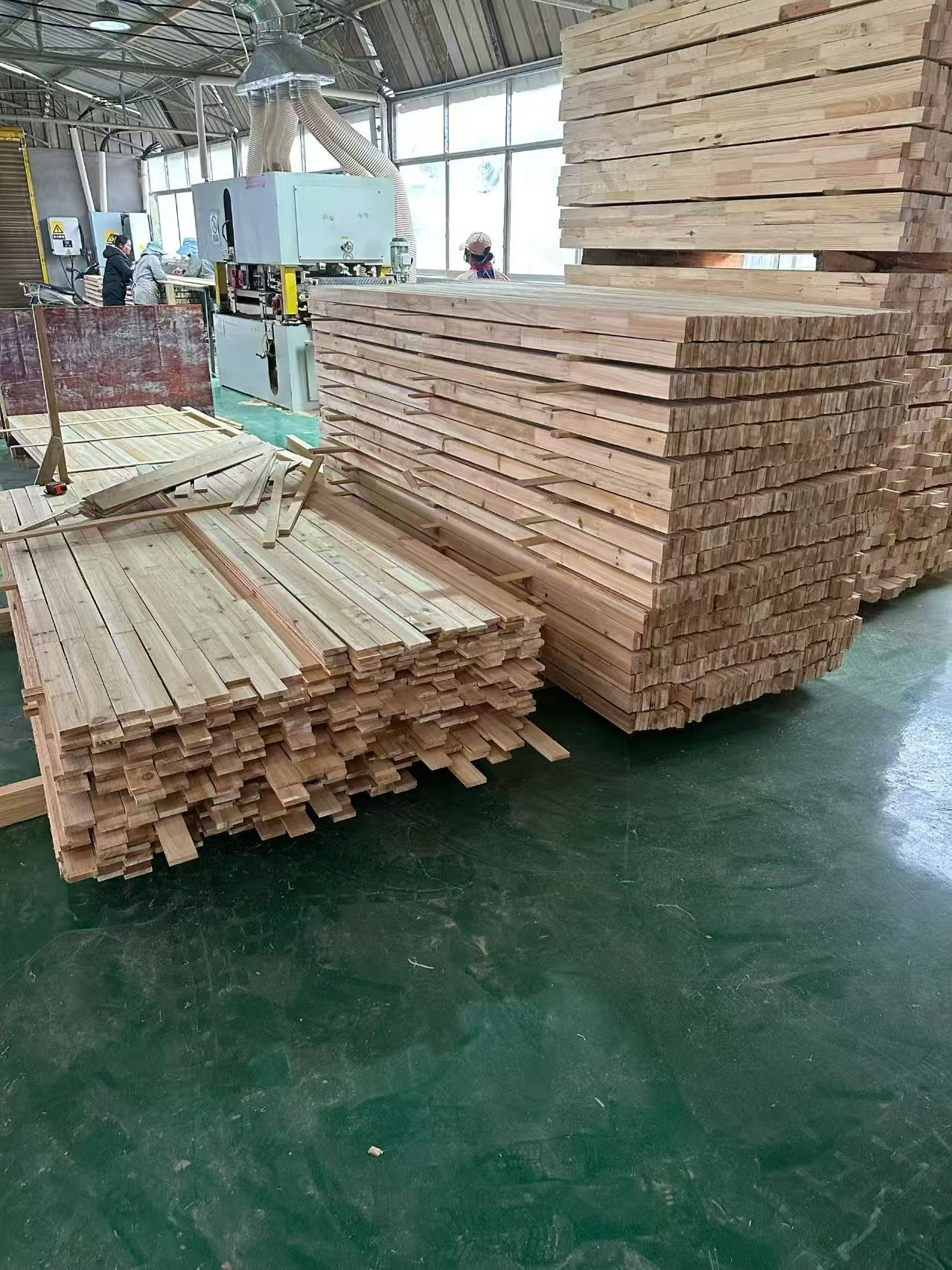
By 2025, China's timber processing industry will exhibit characteristics of large-scale, green, and intelligent development,
leading to structural changes in the industry's structure and operating models.
In terms of scale and layout, the national timber processing market is projected to reach 1.8 trillion yuan, forming industrial clusters centered in Shunde,
Guangdong; Qingdao, Shandong; and Nantong, Jiangsu. Shandong, leveraging its port advantages,
is developing port-adjacent processing parks,
and mergers and acquisitions among leading companies are driving the industry's CR5 concentration to 38%.
On the raw material side, domestic timber production is approximately 120 million cubic meters, with a self-sufficiency rate of 47% and an import dependence of 35%-40%, primarily from Russia and Southeast Asia.
In terms of technology and policy, policies require 80% of large-scale enterprises to complete intelligent transformation,
with CNC equipment penetration reaching 45% and industrial internet remote operation and maintenance systems covering 60%.
Stricter environmental policies, with formaldehyde emission standards increasing by 30%,
are forcing enterprises to increase their annual investment in technological upgrades by 23%,
making formaldehyde-free adhesives and intelligent drying equipment key research and development areas.
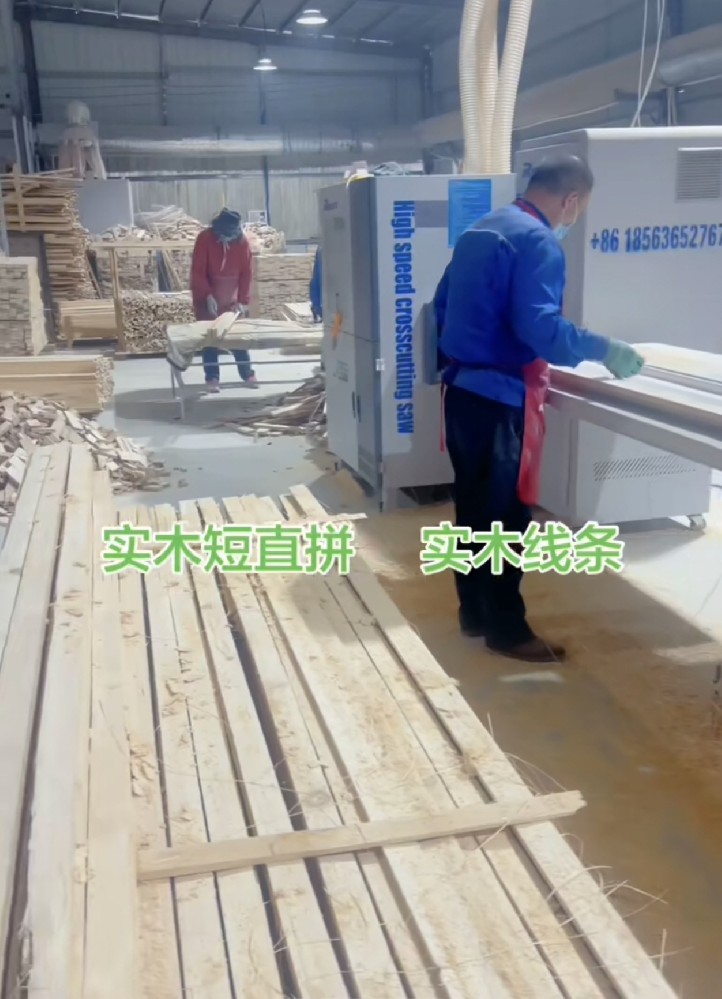

In terms of demand and development trends, the downstream construction (green building,
prefabricated building) and customized furniture markets are the core drivers, with the customized furniture market exceeding 860 billion yuan. On the export side, while benefiting from RCEP, companies need to cope with EU carbon tariffs and new FSC certification regulations. Leading companies are hedging risks through overseas forest land acquisitions and carbon trading. The industry is shifting from resource-dependent to technology-driven.